Distributed SQL Tips and Tricks – Feb 14, 2020
Welcome to this week’s tips and tricks blog where we recap some distributed SQL questions from around the Internet. We’ll also review upcoming events, new documentation and blogs that have been published since the last post. Got questions? Make sure to ask them on our YugabyteDB Slack channel, Forum, GitHub or Stackoverflow. Ok, let’s dive right in:
How can I get the JSON output of distinct columns?
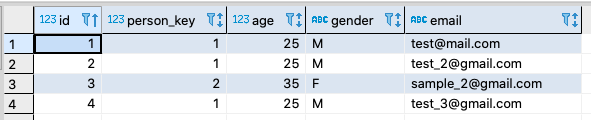
This can be done in YugabyteDB with a combination of aggregation and PostgreSQL’s JSON functions. For example, let’s say we have the following table called students with the data below:
To output to JSON by distinct columns, execute the following:
select
person_key,
json_build_object(
'age', age,
'gender', gender,
'email', json_agg(email order by id)
) js
from students
group by person_key, age, gender
order by person_key;
Which should output:

How do I issue a query that ranks items based on total sales?
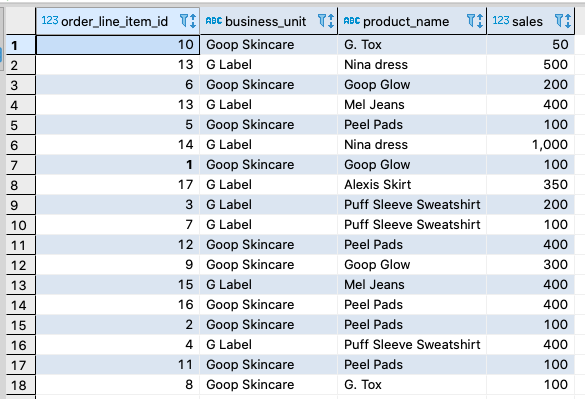
Because YugabyteDB is PostgreSQL-compatible, just like in PostgreSQL, in YugabyteDB you can rank items based on total sales by using the RANK function. For example, let’s say we have the following table called product_sales with the data below:
We can use the following query which makes use of the RANK window function.
SELECT
business_unit,
product_name,
SUM(sales) AS sales,
RANK() OVER(ORDER BY SUM(sales) DESC) ranking
FROM product_sales
GROUP BY business_unit, product_name
ORDER BY ranking, business_unit
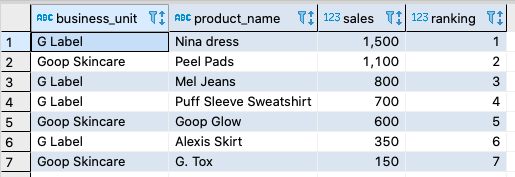
This results in the following ranking based on total sales:
In YugabyteDB, do TRUNCATE and DELETE work like they do in PostgreSQL?
Yes. In general, to remove data from a table, you’ll want to use the DELETE statement with a WHERE clause. However, for a large table, it is often more efficient to use the TRUNCATE TABLE statement. Why? Because the TRUNCATE TABLE statement removes all rows from a table without scanning it. This is the reason why it is faster than the DELETE statement. TRUNCATE is also able to operate on more than one table with a single command.
How do I issue an UPDATE statement and selectively replace specific characters in records that match given criteria?
Just like in PostgreSQL, in YugabyteDB one way you can do this is by using the REGEX_REPLACE function. For example, let’s say we have a table called product_registrations and unfortunately the zeros in the serial numbers were accidentally inputted as “o”.
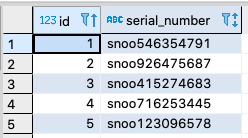
By using the REGEX_REPLACE function we can surgically make the correct substitution.
UPDATE product_registrations SET serial_number = REGEXP_REPLACE(serial_number, '^snoo', 'sn00');
The new output should look like this:

New Documentation, Blogs, Tutorials and Videos
New Blogs
- YugabyteDB Engineering Update – Jan 29, 2020
- Distributed SQL vs. NewSQL
- How to Migrate the Sakila Database from MongoDB to Distributed SQL with Studio 3T
New Videos
- How to Get Started with Distributed SQL on Google Kubernetes Engine
- Developing Microservices with the Google Hipster Demo, Istio and a Distributed SQL Database
- Developing Cloud-Native Spring Microservices with a Distributed SQL Backend
- How to Upgrade a Local YugabyteDB Cluster
New and Updated Docs
- Configure encryption in transit
- Configure encryption at rest
- Deploy on Docker Compose
- Deploy on Google Kubernetes Engine using Helm Chart
Upcoming Meetups and Conferences
PostgreSQL Meetups
- Feb 20: Silicon Valley PostgreSQL Meetup
Distributed SQL Webinars
Conferences
- Postgres Conference, March 23-27, 2020, New York
- KubeCon + CloudNativeCon Europe, March 30 – April 2, 2020, Amsterdam
- Google Cloud Next, April 6-8, 2020, San Francisco
- Red Hat Summit, April 27-29, 2020, San Francisco
We Are Hiring!
Yugabyte is growing fast and we’d like you to help us keep the momentum going! Check out our currently open positions:
- Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) – Sunnyvale, CA
- Community Success Engineer – Remote OK
- Senior Curriculum Developer – Remote OK
- Frontend Engineer – Sunnyvale, CA
- Software Engineer – Cloud Infrastructure – Sunnyvale, CA
- Software Engineer – Core Database – Sunnyvale, CA
- Software Engineer – Full Stack – Sunnyvale, CA
- Solutions Engineer – Sunnyvale, CA
- Developer Advocate – Sunnyvale, CA
Our team consists of domain experts from leading software companies such as Facebook, Oracle, Nutanix, Google and LinkedIn. We have come a long way in a short time but we cannot rest on our past accomplishments. We need your ideas and skills to make us better at every function that is necessary to create the next great software company. All while having tons of fun and blazing new trails!
Get Started
Ready to start exploring YugabyteDB features? Getting up and running locally on your laptop is fast. Visit our quickstart page to get started.
What’s Next?
- Compare YugabyteDB in depth to databases like CockroachDB, Google Cloud Spanner and MongoDB.
- Get started with YugabyteDB on macOS, Linux, Docker and Kubernetes.
- Contact us to learn more about licensing, pricing or to schedule a technical overview.