How-to: The PGExercises PostgreSQL Tutorial Running on a Distributed SQL Database
PgExercises is a sample dataset used to power the PostgreSQL Exercises website. The site is comprised of over 80 exercises designed to be used as a companion to the official PostgreSQL documentation. The exercises on the PGExercises site range from simple SELECT statements and WHERE clauses, through JOINs and CASE statements, then on to aggregations, window functions, and recursive queries.
The dataset consists of 3 tables (members, bookings, and facilities) and table relationships as shown in the ER diagram below:

In this post we are going to walk you through how to download and install PGExercises on the YugabyteDB distributed SQL database with a replication factor of 3.
What’s YugabyteDB? It’s a high performance distributed SQL database for global, internet-scale apps. YugabyteDB is a PostgreSQL-compatible database. Similar to Google Spanner, YugabyteDB gives you all the scalability characteristics of NoSQL, without sacrificing the ACID transactions or strong consistency you are accustomed to with PostgreSQL.
Download and Install YugabyteDB
For complete instructions on how to get up and running on a variety of platforms including prerequisites, check out our Quickstart Guide. In the following section we’ll cover the basic steps for getting up and running in just a few minutes with a local 3 node cluster on your Mac.
Download and Extract YugabyteDB
$ wget https://downloads.yugabyte.com/yugabyte-2.0.1.0-darwin.tar.gz
$ tar xvfz yugabyte-2.0.1.0-darwin.tar.gz && cd yugabyte-2.0.1.0/
Note: The above instructions are for version 1.3.0. To find the latest version of YugabyteDB, visit the quickstart page.
Configure Loopback Addresses
Add a few loopback IP addresses for the various YugabyteDB nodes to use.
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.2
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.3
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.4
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.5
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.6
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.7
Create a 3 Node Cluster
With the command below you’ll create a 3 node cluster with a replication factor of 3.
$ ./bin/yb-ctl --rf 3 create
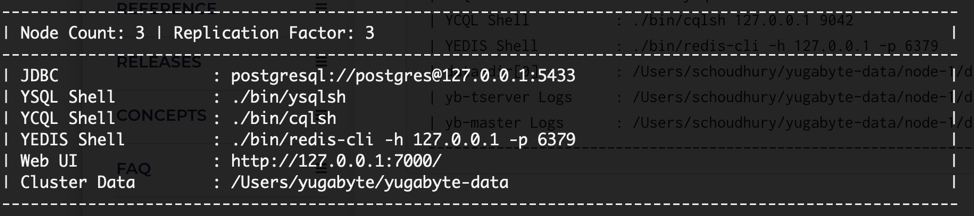
Check the Status of the YugabyteDB Cluster
Now let’s take a look at the status of the cluster and all the nodes that comprise it.
$ ./bin/yb-ctl status
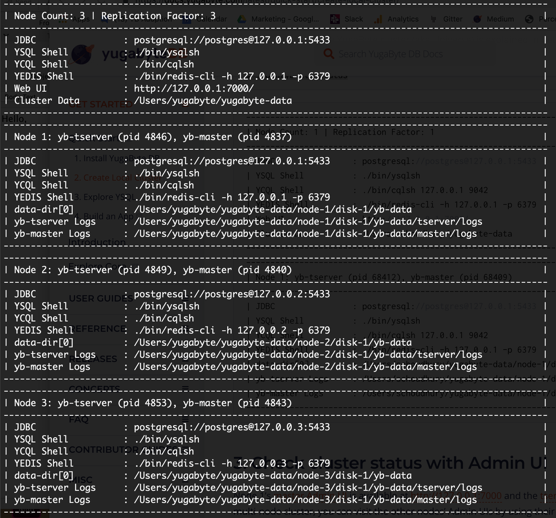
As you can see from the output, we have three nodes running locally with a replication factor of 3. This means that every piece of data is being replicated on all three nodes.
Enter the YSQL shell
Next run the ysqlsh command to enter the PostgreSQL shell.
$ ./bin/ysqlsh --echo-queries
ysqlsh (11.2)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=#
What’s YSQL? It’s YugabyteDB’s PostgreSQL-compatible, distributed SQL API.
We are now ready to build the PGExercises database.
Download and Install the PGExercises Database
Download the PGExercises Scripts
You can download the PGExercises database that is compatible with YugabyteDB from our GitHub repo. The two files are:
- clubdata_ddl.sql which creates tables and other database objects
- clubdata_data.sql which loads the sample data into the exercises database
Create the Exercises Database
CREATE DATABASE exercises;
Let’s confirm we have the exercises database by listing out the databases on our cluster.
postgres=# \l
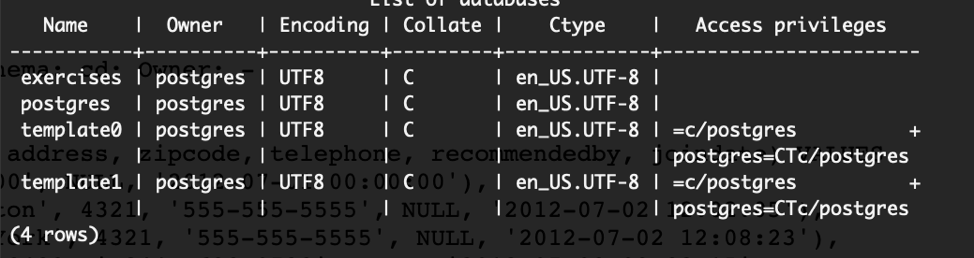
Switch to the exercises database.
postgres=# \c exercises
You are now connected to database "exercises" as user "postgres".
exercises=#
Build the Exercises Tables and Objects
exercises=# \i /Users/yugabyte/clubdata_ddl.sql
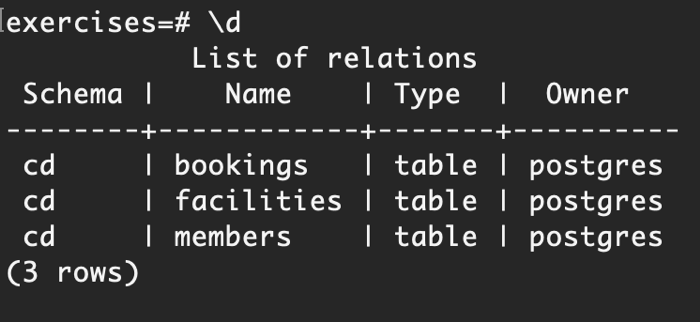
We can verify that all 3 of our tables have been created by executing:
exercises=# \d
Load Sample Data into Exercises
Next, let’s load our database with sample data.
exercises=# \i /Users/yugabyte/clubdata_data.sql
Let’s do a simple SELECT to pull data from the bookings table to verify we now have some data to play with.
exercises=# SELECT * FROM bookings LIMIT 5;
Try the PGExercises Tutorial
That’s it! You are ready to start working through the PGExercises tutorial with YugabyteDB as the backend. PGExercises is made up of 81 exercises and broken into the following major sections:
- Simple SQL Queries
- JOINs and Subqueries
- Modifying Data
- Aggregation
- Working with Timestamps
- String Operations
- Recursive Queries
Note that all of the exercises on the site will work with YugabyteDB with the exception of the following:
- This JOIN example has a bug and won’t return the correct row numbers. The GitHub issue can be tracked here.
- In this string operation exercise you might notice that our sort order will be different. This is because we hash partition our data. As a result, row ordering is expected to be different.
- In the calculated UPDATE example, you will get an error because “FROM clause in UPDATE” is not yet supported. You can track the issue on GitHub here.
- The exercise which demonstrates a DELETE based on a subquery will return an error. You can track the resolution of this issue on GitHub here.
What’s Next
- Compare YugabyteDB in depth to databases like CockroachDB, Google Cloud Spanner and MongoDB.
- Get started with YugabyteDB on macOS, Linux, Docker, and Kubernetes.
- Contact us to learn more about licensing, pricing or to schedule a technical overview.


