Cloud Native Java: Integrating YugabyteDB with Spring Boot, Quarkus, and Micronaut
Java is the quintessential language runtime for enterprise applications built on monoliths, microservices, and modular architecture patterns. But when it comes to “Enterprise Java,” Spring is the de facto framework of choice.
The Spring ecosystem—with the simplicity of Spring Boot—has grown to provide integration touchpoints to a majority of the Java ecosystem. For starters, it offers a clean abstraction and “glue” code to build cohesive enterprise applications. However, as the ecosystem evolves, two newer frameworks are growing in popularity: Quarkus and Micronaut.
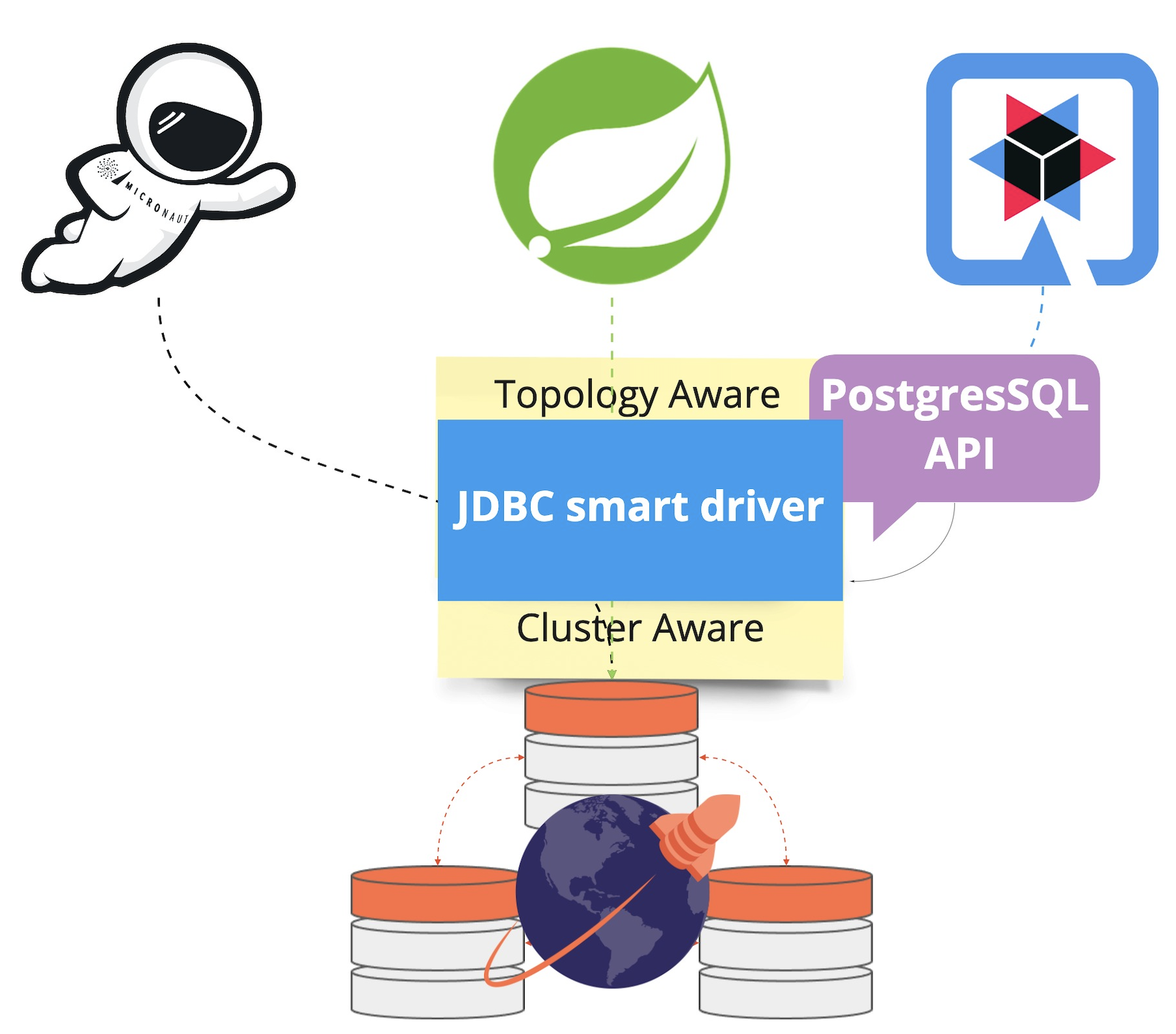
Spring Boot, Quarkus, and Micronaut are seeing massive adoption for cloud native greenfield applications, as well as brownfield modernization efforts. In this blog post, we look at how YugabyteDB’s YSQL smart driver integrates with all three popular microservices frameworks.
Prerequisites
- Follow the YB Quickstart instructions to run a local YugabyteDB cluster. Test YugabyteDB’s YSQL API to confirm you have a YSQL service running on “localhost:5433”.
- You will need JDK 11 or above. You can use SDKMAN to install the JDK runtime.
Getting started
You can find the complete source code in this GitHub repository. This project has directories for all three frameworks: spring-boot, quarkus, and micronaut. Clone this repository to a local workstation and open the “yb-ms-data” directory in your favorite IDE to easily navigate and explore framework-specific code.
| git clone
This source repository consists of a simple JPA-based web application with CRUD functionality. We will focus in this blog only on the database integration point.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applications that you can “just run.”
The following section describes how to build a simple JPA-based web application with the Spring Boot framework for YSQL API using the YugabyteDB JDBC Driver.
For starters, navigate to the springboot framework folder inside the project yb-ms-data directory.
| cd yb-ms-data/springboot
Dependencies
This project depends on the following libraries:
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator")
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa")
implementation("org.flywaydb:flyway-core")
implementation("org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-ui:1.5.9")
implementation("com.yugabyte:spring-data-yugabytedb-ysql:2.3.0") {
exclude(module = "jdbc-yugabytedb")
}
implementation("org.springframework.retry:spring-retry")
annotationProcessor("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-configuration-processor")
annotationProcessor("org.projectlombok:lombok")
developmentOnly("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools")
compileOnly("org.projectlombok:lombok")
runtimeOnly("io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-prometheus")
implementation("com.yugabyte:jdbc-yugabytedb:42.3.3")
testImplementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test")
testImplementation("org.flywaydb.flyway-test-extensions:flyway-spring-test:7.0.0")
testImplementation("com.yugabyte:testcontainers-yugabytedb:1.0.0-beta-4")
testImplementation("org.testcontainers:junit-jupiter:1.15.3")Update the driver dependency library “com.yugabyte:jdbc-yugabytedb:42.3.3” to the latest version. Grab the latest version from YugabyteDB JDBC Driver.
Driver configuration
Refer to the file yb-ms-data/springboot/src/main/resources/application.yaml in the project directory:
spring: jpa: properties: hibernate: connection: provider_disables_autocommit: true default_schema: todo open-in-view: false datasource: url: jdbc:yugabytedb://[hostname:port]/yugabyte?load-balance=true username: yugabyte password: yugabyte driver-class-name: com.yugabyte.Driver hikari: minimum-idle: 5 maximum-pool-size: 20 auto-commit: false
urlis the JDBC connection string. You can set YugabyteDB driver-specific properties such as “load-balance” and “topology-keys” as part of this string.driver-class-nameis the JDBC driver class name.
Update the JDBC URL with the appropriate “hostname” and “port” number details “jdbc:yugabytedb://[hostname: port]/yugabyte” in the application.yaml file. Remember to remove the square brackets. It’s a placeholder to indicate the fields that need user inputs.
Build and run the application
Navigate to the springboot folder: cd yb-ms-data/springboot To build the application: gradle build To run and test the application: gradle bootRun
Quarkus
Quarkus is a Kubernetes Native Java stack tailored for OpenJDK HotSpot and GraalVM. It’s crafted from best-of-breed Java libraries and standards.
This section describes how to build a simple JPA-based web application with the Quarkus framework for YSQL API using the YugabyteDB JDBC Driver.
For starters, navigate to the quarkus framework folder inside the project yb-ms-data directory.
| cd yb-ms-data/quarkus
Dependencies
This project depends on the following libraries:
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-hibernate-orm")
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-flyway")
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-resteasy")
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-resteasy-jackson")
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-config-yaml")
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-agroal")
implementation("io.quarkus:quarkus-smallrye-fault-tolerance")
implementation("com.yugabyte:jdbc-yugabytedb:42.3.3")Update the driver dependency library “com.yugabyte:jdbc-yugabytedb:42.3.3” to the latest version. Grab the latest version from YugabyteDB JDBC Driver.
Driver configuration
Refer to the file yb-ms-data/quarkus/src/main/resources/application.yaml in the project directory:
quarkus: datasource: db-kind: pgsql jdbc: url: jdbc:yugabytedb://[hostname:port]/yugabyte driver: com.yugabyte.Driver initial-size: 5 max-size: 20 additional-jdbc-properties: load-balance: true
db-kindindicates the type of db instance. The value can be pqsql or postgresql for PostgreSQL or PostgreSQL API-compatible instances. You can have either of these values as YugabyteDB is PostgreSQL-compliant and reuses the PostgreSQL query layer.urldriveris the JDBC driver class name.additional-jdbc-propertiesis where YugabyteDB driver-specific properties such as “load-balance” and “topology-keys” can be set.
Next, update the JDBC URL with the appropriate “hostname” and “port” number details “jdbc:yugabytedb://[hostname: port]/yugabyte” in the application.yaml file. Remember to remove the square brackets. It is a placeholder to indicate the fields that need user inputs.
Build and run the application
Navigate to the quarkus folder: cd yb-ms-data/quarkus To build the application: gradle quarkusBuild To run and test the application: gradle quarkusDev
Micronaut
Micronaut is a modern, JVM-based, full-stack framework for building modular, easily-testable microservice and serverless applications.
This section describes how to build a simple JPA-based web application with the Micronaut framework for YSQL API using the YugabyteDB JDBC Driver.
Navigate to the micronaut framework folder inside the project yb-ms-data directory.
| cd yb-ms-data/micronaut
Dependencies
This project depends on the following libraries:
annotationProcessor("io.micronaut:micronaut-http-validation")
annotationProcessor("io.micronaut.data:micronaut-data-processor")
annotationProcessor("io.micronaut.openapi:micronaut-openapi")
implementation("io.micronaut:micronaut-http-client")
implementation("io.micronaut:micronaut-management")
implementation("io.micronaut:micronaut-runtime")
implementation("io.micronaut.data:micronaut-data-hibernate-jpa")
implementation("io.micronaut.flyway:micronaut-flyway")
implementation("io.micronaut.sql:micronaut-jdbc-hikari")
implementation("io.swagger.core.v3:swagger-annotations")
implementation("javax.annotation:javax.annotation-api")
runtimeOnly("ch.qos.logback:logback-classic")
implementation("io.micronaut:micronaut-validation")
implementation("com.yugabyte:jdbc-yugabytedb:42.3.3")Update the driver dependency library “com.yugabyte:jdbc-yugabytedb:42.3.3” to the latest version. Grab the latest version from YugabyteDB JDBC driver.
Driver Configuration
Refer to the file yb-ms-data/micronaut/src/main/resources/application.yaml in the project directory:
datasources: default: url: jdbc:yugabytedb://[hostname:port]/yugabyte driverClassName: com.yugabyte.Driver data-source-properties: load-balance: true currentSchema: todo username: yugabyte password: yugabyte minimum-idle: 5 maximum-pool-size: 20
urlis the JDBC connection string.driverClassNameis the JDBC driver class name.data-source-properties
Update the JDBC URL with the appropriate “hostname” and “port” number details “jdbc:yugabytedb://[hostname: port]/yugabyte”
Build and run the application
Navigate to the micronaut folder: cd yb-ms-data/micronaut To build the application: gradle build To run and test the application: gradle run
Conclusion
This post looked at how we can quickly get started with popular cloud native java frameworks using the YugabyteDB JDBC driver without any application-level modifications.
YSQL’s API compatibility with PostgreSQL accelerates developer productivity and onboarding. By integrating with the existing ecosystem, YugabyteDB ensures developers can quickly start using a language they already know and love.
The YugabyteDB JDBC driver is a distributed driver built on the PostgreSQL driver. Although the upstream PostgreSQL JDBC driver works with YugabyteDB, the YugabyteDB driver enhances it by providing additional features such as cluster and topology awareness.
If you haven’t already, check out our Docs site to learn more about YugabyteDB. Any questions? Ask them in the YugabyteDB community Slack channel.


